RESONEUT: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Schematic cross-section of RESONEUT.png|thumb|right|Schematic cross-section of RESONEUT<ref name="NIMA" />]] | [[File:Schematic cross-section of RESONEUT.png|thumb|right|Schematic cross-section of RESONEUT<ref name="NIMA" />]] | ||
RESONEUT <ref name="NIMA"> L. T. Baby, S. A. Kuvin, I. Wiedenhover ''et al.'', Nulc. Inst. Meth. Phys. A, '''877''', 34 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2017.09.019 </ref> is built for spectroscopy of low-lying proton resonances using (d,n) reactions in inverse kinematics with radioactive beams. The setup consists of 9 '''p-terphenyl''' scintillator crystals as neutron detectors placed 23 cm upstream of the target, along with silicon strip detectors, a gas ionization chamber, and NaI detectors. The p-terphenyl crystals provide good detection efficiency for low-energy neutrons below 300 keV emitted at backward angles in the reactions of interest. Pulse shape discrimination is used to distinguish neutrons from gamma background. Experiments were performed with stable | RESONEUT <ref name="NIMA"> L. T. Baby, S. A. Kuvin, I. Wiedenhover ''et al.'', Nulc. Inst. Meth. Phys. A, '''877''', 34 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2017.09.019 </ref> is built for spectroscopy of low-lying proton resonances using (d,n) reactions in inverse kinematics with radioactive beams. The setup consists of 9 '''p-terphenyl''' scintillator crystals as neutron detectors placed 23 cm upstream of the target, along with silicon strip detectors, a gas ionization chamber, and NaI detectors. The p-terphenyl crystals provide good detection efficiency for low-energy neutrons below 300 keV emitted at backward angles in the reactions of interest. Pulse shape discrimination is used to distinguish neutrons from gamma background. Experiments were performed with stable <sup>12</sup>C beams on deuterated targets, populating proton resonances in <sup>13</sup>N. The setup achieved '''~200 keV energy resolution''', a detection efficiency of around '''0.5% per crystal''', and a total efficiency of around 2-5% depending on neutron energy. Overall this provides a compact, high-efficiency system to study low-lying resonances with radioactive beams using (d,n) reactions. | ||
Latest revision as of 20:13, 24 October 2023
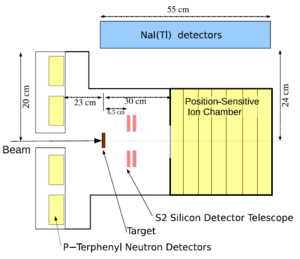
RESONEUT [1] is built for spectroscopy of low-lying proton resonances using (d,n) reactions in inverse kinematics with radioactive beams. The setup consists of 9 p-terphenyl scintillator crystals as neutron detectors placed 23 cm upstream of the target, along with silicon strip detectors, a gas ionization chamber, and NaI detectors. The p-terphenyl crystals provide good detection efficiency for low-energy neutrons below 300 keV emitted at backward angles in the reactions of interest. Pulse shape discrimination is used to distinguish neutrons from gamma background. Experiments were performed with stable 12C beams on deuterated targets, populating proton resonances in 13N. The setup achieved ~200 keV energy resolution, a detection efficiency of around 0.5% per crystal, and a total efficiency of around 2-5% depending on neutron energy. Overall this provides a compact, high-efficiency system to study low-lying resonances with radioactive beams using (d,n) reactions.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 L. T. Baby, S. A. Kuvin, I. Wiedenhover et al., Nulc. Inst. Meth. Phys. A, 877, 34 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2017.09.019