NSCL DAQ: Difference between revisions
| (39 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Introduction = | |||
NSCL DAQ is the Data Acquisition system developed from [https://nscl.msu.edu/ NSCL], MSU. The NSCL DAQ have a [https://docs.nscl.msu.edu/daq/newsite/index.php webpage] (but not very useful for beginner). | |||
People can send emails to mailto:daqhelp@frib.msu.edu for help. | |||
* add neuro debain repository (when the following command fail, go to [http://neuro.debian.net/] | = Installation = | ||
wget -O- http://neuro.debian.net/lists/focal.us-tn.libre | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/neurodebian.sources.list | |||
sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkps://keyserver.ubuntu.com 0xA5D32F012649A5A9 | == Normal installation in Ubuntu 20.04 == | ||
Please see <b>[https://fsunuc.physics.fsu.edu/elog/Pixie_NSCLDAQ/6 this elog entry]</b>. | |||
== using Singularity-container in Ubuntu or Debian == | |||
In order to run the NSCLDAQ in a container (or a VM, Virtual Machine). We need 3 things, | |||
# The container program, we are using [https://sylabs.io/guides/3.5/user-guide/index.html singularity container] | |||
# The OS image for the container, which is Debian 8 or 10 for NSCLDAQ | |||
# The compiled NSCLDAQ for the corresponding OS. | |||
=== Install Singularity-container === | |||
This can be done by source following [https://docs.sylabs.io/guides/3.0/user-guide/installation.html#install-on-linux Sylabs Documentation]. The installation process requires some dependencies from the apt repository as well as installing and configuring Go. An alternative method using a debian repository is shown below. | |||
* add neuro debain repository (when the following command fail, go to [http://neuro.debian.net/ Neuro Debian website] | |||
~>wget -O- http://neuro.debian.net/lists/focal.us-tn.libre | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/neurodebian.sources.list | |||
~>sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkps://keyserver.ubuntu.com 0xA5D32F012649A5A9 | |||
* update the repository | * update the repository | ||
sudo apt update | ~>sudo apt update | ||
* install singularity | * install singularity | ||
sudo apt install signularity-container | ~>sudo apt install signularity-container | ||
=== | === Download the OS image === | ||
Like any Virtual Machine, we need an OS for it to run. NSCL DAQ works on Debian 8 or 10. | |||
/usr/opt>singularity build nscl-buster.img docker://fribdaq/frib-buster:XXX | |||
/usr/opt>singularity build nscl-jessie.img docker://fribdaq/frib-jessie:XXX | |||
[https://sourceforge.net/projects/nscldaq/files/for-containers/usropt-jessie.tar.gz | where XXX is the version, please check [https://hub.docker.com/r/fribdaq/frib-jessie/tags Jessie here] and [https://hub.docker.com/r/fribdaq/frib-buster/tags Buster here] | ||
=== to test the singularity is working === | |||
anywhere>singularity shell /usr/opt/nscl-jessie.img | |||
you will bring to the singularity interactive shell | |||
Singularity: Invoking an interactive shell within container... | |||
Singularity nscl-jessie.img:~> | |||
We can check the OS by | |||
Singularity nscl-jessie.img:~>lsb_release -a | |||
No LSB modules are available. | |||
Distributor ID: Debian | |||
Description: Debian GNU/Linux 8.11 (jessie) | |||
Release: 8.11 | |||
Codename: jessie | |||
That means we have a running jessie. | |||
=== Download the compiled NSCLDAQ === | |||
The last thing we need is a per-compiled NSCLDAQ | |||
[https://sourceforge.net/projects/nscldaq/files/for-containers/usropt-jessie.tar.gz Link to download Debian 8 Jessie] | |||
[https://sourceforge.net/projects/nscldaq/files/for-containers/ Link to download Debian 10 buster] | |||
And decompress it into /usr/opt/ -> so that the path is /usr/opt/opt-jessie | And decompress it into /usr/opt/ -> so that the path is /usr/opt/opt-jessie | ||
=== | === To run NSCL DAQ === | ||
==== run in interactive shell ==== | |||
Singularity allows user to "mount" the host system directory by using '''--bind''' option. | |||
In the following, we will bind the /usr/opt/opt-jessie to /usr/opt/, which is in the VM | |||
~>singularity shell --bind /usr/opt/opt-jessie:/usr/opt /usr/opt/nscl-jessie.img | |||
after entered the shell, we check | |||
Singularity nscl-jessie.img:~> ls /usr/opt/ | |||
caendigitizerlibs epics iseg plx | |||
caenhv-5.22 epicstcl iseg-beta PLX7 | |||
caenhv-5.82 geco JESSIE root | |||
cmake genx mesycontrol-1.0.4-x86_64 spectcl | |||
daq GET mpi xiaapi | |||
ddas gretina mpitcl | |||
ddastoys gretinaglom nscldaq | |||
ddastoys.saved gsl NSCLGET | |||
The NSCLDAQ runs on 3 major components | |||
# DaqPortManager | |||
# RingMaster | |||
# ReadOutShell | |||
and since we are in the interactive singularity shell, we can run it without a problem. | |||
==== run in background ==== | |||
We can use the '''exec''' option to run the DAQ without going into the VM or singularity shell. | |||
It is more easy to have a bash script to do it for us. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="Bash" line> | |||
#!/bin/bash | |||
export USROPT=/usr/opt/opt-jessie/ | |||
export SINGULARITY_CONTAINER=/usr/opt/nscl-jessie.img | |||
export DAQPORTMANAGER=/usr/opt/daq/11.3-023/bin/DaqPortManager | |||
export DAQPORTMANAGERLOGFILE=$HOME/daq.log | |||
export DAQPORTMANAGERPIDFILE=$HOME/daq.pid | |||
export RINGMASTER=/usr/opt/daq/11.3-023/bin/RingMaster | |||
export RINGMASTERLOGFILE=$HOME/ring.log | |||
nohup singularity exec --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER} ${DAQPORTMANAGER} -log ${DAQPORTMANAGERLOGFILE} -pidfile ${DAQPORTMANAGERPIDFILE} </dev/null >/dev/null 2>&1 & | |||
echo $! > nscl_pid.txt | |||
nohup singularity exec --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER} ${RINGMASTER} -f ${RINGMASTERLOGFILE} </dev/null >/dev/null 2>&1 & | |||
echo $! >> nscl_pid.txt | |||
echo "============= here are the PID for the DaqPortManager and RingMaster" | |||
cat nscl_pid.txt | |||
#singularity exec --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER} ${DAQPORTMANAGER} -log ${DAQPORTMANAGERLOGFILE} -pidfile ${DAQPORTMANAGERPIDFILE} | |||
#singularity shell --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt/ ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
I saved this bash script as ~/start_nscldaq.sh | |||
To run it, we need sudo, otherwise, the DaqPortManager compiles that it does not have permission to /var/tmp/daqportmgr/listen.port | |||
We can check the DaqPortManager and RingMaster are running by | |||
ps -ef | grep -E 'Daq*|Ring*' | |||
<span style="color:red">it seems that it opens two instants of VM, one is running DaqPortManager and another is running RingMaster, How can they communicate? </span> | |||
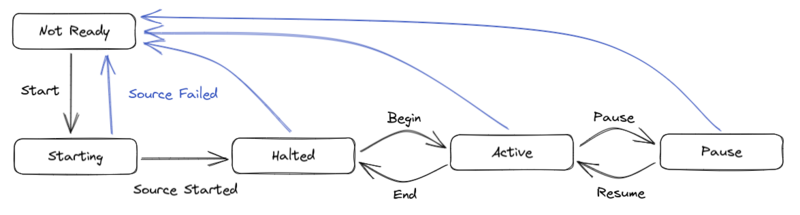
= ReadOutShell = | |||
See [[Pixie16_digitizer#ReadOutShell | the Pixie16 ReadoutShell setup]] for the moment. | |||
Also see [https://docs.nscl.msu.edu/daq/newsite/nscldaq-11.4/c3683.html this from NSCL offical webpage] | |||
[[File:StateDiagramofReadoutShell.png|800px|frameless|none|StateDiagram of ReadoutShell]] | |||
= NSCLDAQ evt file = | |||
The NSCL DAQ output the data file as *.evt. It is different from the PIXIE evt file. | |||
More information can be found in [https://docs.nscl.msu.edu/daq/newsite/ddas-1.1/Data_01Format.html Data Format]. | |||
The evt file can be view as 4 bytes (32 bits, int) array | |||
{|class='wikitable' | |||
! Group|| Item || Bytes || word | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="2" | Ring Item Header || size || 4 || 1 | |||
|- | |||
| type (30 for physics event) || 4 || 2 | |||
|- | |||
|rowspan="4" | Ring Item Body Header || size || 4 || 3 | |||
|- | |||
| timestamp || 8 || 4,5 | |||
|- | |||
| source ID || 4 || 6 | |||
|- | |||
| barrier type || 4 || 7 | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="10" | Ring Item Body || size || 4 || 8 | |||
|- | |||
| fragment #0 || 56+ | |||
|- | |||
| fragment #1 || 56+ | |||
|- | |||
| fragment #2 || 56+ | |||
|- | |||
| .... || | |||
|- | |||
| fragment #n || 56+ | |||
|} | |||
{| class='wikitable' | |||
! Fragment Group || colspan="2"|Item || Byte || word | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4" | Fragment Header || colspan="2"|Timestamp || 8 || 1,2 | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|source ID || 4 || 3 | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|Payload size in bytes || 4 || 4 | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|Barrier Type || 4 || 5 | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="10" |Fragment Payload || rowspan="2"| Ring Item Header || size || 4 || 6 | |||
|- | |||
| type (20 = physics item) || 4 || 7 | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4"| Ring Item Body Header || size || 4 || 8 | |||
|- | |||
| Timestamp || 8 || 9, 10 | |||
|- | |||
| Source ID || 4 || 11 | |||
|- | |||
| Barrier Type || 4 || 12 | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="4"| Ring Item Body || size || 4 || 13 | |||
|- | |||
| Device Info || 4 || 14 | |||
|- | |||
| '''Raw Data''' || | |||
|} | |||
For the Pixie digitizer, the structure of the '''Raw Data''' can be found [[Pixie16_digitizer#Data_Structure | Pixie16 digitizer ]] | |||
From the above table, the '''Ring Item''' are repeated on the top level and also inside the fragment. | |||
The top level '''Ring Item Header/type''' is used to identify the type of the Ring item | |||
{| class ='wikitable' | |||
! '''Ring Item Header/type''' value || Meaning | |||
|- | |||
| 1 || Run Begin | |||
|- | |||
| 2 || Run End | |||
|- | |||
| 3 || Run Pause | |||
|- | |||
| 4 || Run Resume | |||
|- | |||
| 20 || Scaler found | |||
|- | |||
| 30 || Physics event | |||
|- | |||
| others || untreated ring item | |||
|} | |||
When the '''Ring Item Header/type''' is not 30, the '''Ring Item Header/size''' - 8 bits data should be skipped. | |||
Latest revision as of 18:55, 4 November 2022
Introduction
NSCL DAQ is the Data Acquisition system developed from NSCL, MSU. The NSCL DAQ have a webpage (but not very useful for beginner).
People can send emails to mailto:daqhelp@frib.msu.edu for help.
Installation
Normal installation in Ubuntu 20.04
Please see this elog entry.
using Singularity-container in Ubuntu or Debian
In order to run the NSCLDAQ in a container (or a VM, Virtual Machine). We need 3 things,
- The container program, we are using singularity container
- The OS image for the container, which is Debian 8 or 10 for NSCLDAQ
- The compiled NSCLDAQ for the corresponding OS.
Install Singularity-container
This can be done by source following Sylabs Documentation. The installation process requires some dependencies from the apt repository as well as installing and configuring Go. An alternative method using a debian repository is shown below.
- add neuro debain repository (when the following command fail, go to Neuro Debian website
~>wget -O- http://neuro.debian.net/lists/focal.us-tn.libre | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/neurodebian.sources.list ~>sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkps://keyserver.ubuntu.com 0xA5D32F012649A5A9
- update the repository
~>sudo apt update
- install singularity
~>sudo apt install signularity-container
Download the OS image
Like any Virtual Machine, we need an OS for it to run. NSCL DAQ works on Debian 8 or 10.
/usr/opt>singularity build nscl-buster.img docker://fribdaq/frib-buster:XXX /usr/opt>singularity build nscl-jessie.img docker://fribdaq/frib-jessie:XXX
where XXX is the version, please check Jessie here and Buster here
to test the singularity is working
anywhere>singularity shell /usr/opt/nscl-jessie.img
you will bring to the singularity interactive shell
Singularity: Invoking an interactive shell within container... Singularity nscl-jessie.img:~>
We can check the OS by
Singularity nscl-jessie.img:~>lsb_release -a No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Debian Description: Debian GNU/Linux 8.11 (jessie) Release: 8.11 Codename: jessie
That means we have a running jessie.
Download the compiled NSCLDAQ
The last thing we need is a per-compiled NSCLDAQ
Link to download Debian 8 Jessie
Link to download Debian 10 buster
And decompress it into /usr/opt/ -> so that the path is /usr/opt/opt-jessie
To run NSCL DAQ
run in interactive shell
Singularity allows user to "mount" the host system directory by using --bind option.
In the following, we will bind the /usr/opt/opt-jessie to /usr/opt/, which is in the VM
~>singularity shell --bind /usr/opt/opt-jessie:/usr/opt /usr/opt/nscl-jessie.img
after entered the shell, we check
Singularity nscl-jessie.img:~> ls /usr/opt/ caendigitizerlibs epics iseg plx caenhv-5.22 epicstcl iseg-beta PLX7 caenhv-5.82 geco JESSIE root cmake genx mesycontrol-1.0.4-x86_64 spectcl daq GET mpi xiaapi ddas gretina mpitcl ddastoys gretinaglom nscldaq ddastoys.saved gsl NSCLGET
The NSCLDAQ runs on 3 major components
- DaqPortManager
- RingMaster
- ReadOutShell
and since we are in the interactive singularity shell, we can run it without a problem.
run in background
We can use the exec option to run the DAQ without going into the VM or singularity shell.
It is more easy to have a bash script to do it for us.
#!/bin/bash
export USROPT=/usr/opt/opt-jessie/
export SINGULARITY_CONTAINER=/usr/opt/nscl-jessie.img
export DAQPORTMANAGER=/usr/opt/daq/11.3-023/bin/DaqPortManager
export DAQPORTMANAGERLOGFILE=$HOME/daq.log
export DAQPORTMANAGERPIDFILE=$HOME/daq.pid
export RINGMASTER=/usr/opt/daq/11.3-023/bin/RingMaster
export RINGMASTERLOGFILE=$HOME/ring.log
nohup singularity exec --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER} ${DAQPORTMANAGER} -log ${DAQPORTMANAGERLOGFILE} -pidfile ${DAQPORTMANAGERPIDFILE} </dev/null >/dev/null 2>&1 &
echo $! > nscl_pid.txt
nohup singularity exec --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER} ${RINGMASTER} -f ${RINGMASTERLOGFILE} </dev/null >/dev/null 2>&1 &
echo $! >> nscl_pid.txt
echo "============= here are the PID for the DaqPortManager and RingMaster"
cat nscl_pid.txt
#singularity exec --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER} ${DAQPORTMANAGER} -log ${DAQPORTMANAGERLOGFILE} -pidfile ${DAQPORTMANAGERPIDFILE}
#singularity shell --bind ${USROPT}:/usr/opt/ ${SINGULARITY_CONTAINER}
I saved this bash script as ~/start_nscldaq.sh
To run it, we need sudo, otherwise, the DaqPortManager compiles that it does not have permission to /var/tmp/daqportmgr/listen.port
We can check the DaqPortManager and RingMaster are running by
ps -ef | grep -E 'Daq*|Ring*'
it seems that it opens two instants of VM, one is running DaqPortManager and another is running RingMaster, How can they communicate?
ReadOutShell
See the Pixie16 ReadoutShell setup for the moment.
Also see this from NSCL offical webpage
NSCLDAQ evt file
The NSCL DAQ output the data file as *.evt. It is different from the PIXIE evt file.
More information can be found in Data Format.
The evt file can be view as 4 bytes (32 bits, int) array
| Group | Item | Bytes | word |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ring Item Header | size | 4 | 1 |
| type (30 for physics event) | 4 | 2 | |
| Ring Item Body Header | size | 4 | 3 |
| timestamp | 8 | 4,5 | |
| source ID | 4 | 6 | |
| barrier type | 4 | 7 | |
| Ring Item Body | size | 4 | 8 |
| fragment #0 | 56+ | ||
| fragment #1 | 56+ | ||
| fragment #2 | 56+ | ||
| .... | |||
| fragment #n | 56+ |
| Fragment Group | Item | Byte | word | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragment Header | Timestamp | 8 | 1,2 | |
| source ID | 4 | 3 | ||
| Payload size in bytes | 4 | 4 | ||
| Barrier Type | 4 | 5 | ||
| Fragment Payload | Ring Item Header | size | 4 | 6 |
| type (20 = physics item) | 4 | 7 | ||
| Ring Item Body Header | size | 4 | 8 | |
| Timestamp | 8 | 9, 10 | ||
| Source ID | 4 | 11 | ||
| Barrier Type | 4 | 12 | ||
| Ring Item Body | size | 4 | 13 | |
| Device Info | 4 | 14 | ||
| Raw Data | ||||
For the Pixie digitizer, the structure of the Raw Data can be found Pixie16 digitizer
From the above table, the Ring Item are repeated on the top level and also inside the fragment.
The top level Ring Item Header/type is used to identify the type of the Ring item
| Ring Item Header/type value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1 | Run Begin |
| 2 | Run End |
| 3 | Run Pause |
| 4 | Run Resume |
| 20 | Scaler found |
| 30 | Physics event |
| others | untreated ring item |
When the Ring Item Header/type is not 30, the Ring Item Header/size - 8 bits data should be skipped.