Ion Sources: Difference between revisions
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
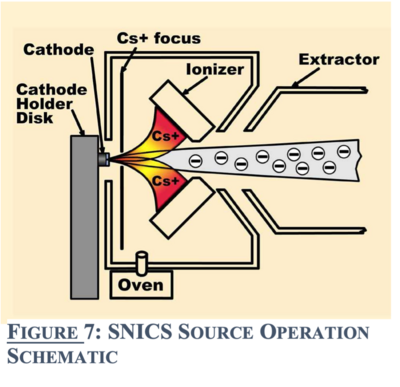
[[File:SNIC operation.png|400px|thumb|right|Sputter source Operation schematic]] | [[File:SNIC operation.png|400px|thumb|right|Sputter source Operation schematic]] | ||
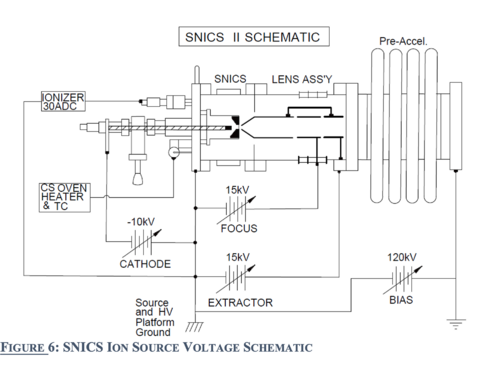
[[File:SNICS ionSourceVolatge.png|500px|thumb|Sputter source Volatge Schematic]] | [[File:SNICS ionSourceVolatge.png|500px|thumb|Sputter source Volatge Schematic]] | ||
Sputter Source is also called SNICS. | |||
== Operation == | |||
The Source of Negative Ions by Cesium Sputtering (SNICS) produces a negative ion beam. A reservoir of cesium metal is heated so that cesium vapor is formed. This cesium vapor comes from the cesium oven into an enclosed area between the cooled cathode and the heated ionizing surface. Some cesium condenses onto the cool surface of the cathode and some of the cesium is ionized by the hot surface. The positively charged ionized cesium accelerates towards the cathode, sputtering material from the cathode at impact. Some materials will preferentially sputter neutral or positive particles which pick up electrons as they pass through the condensed cesium layer on the surface of the cathode, producing the negatively charged beam. | |||
== Tuning Beam out of the SNICS Source == | |||
Revision as of 17:17, 8 April 2022
Sputter Source
Sputter Source is also called SNICS.
Operation
The Source of Negative Ions by Cesium Sputtering (SNICS) produces a negative ion beam. A reservoir of cesium metal is heated so that cesium vapor is formed. This cesium vapor comes from the cesium oven into an enclosed area between the cooled cathode and the heated ionizing surface. Some cesium condenses onto the cool surface of the cathode and some of the cesium is ionized by the hot surface. The positively charged ionized cesium accelerates towards the cathode, sputtering material from the cathode at impact. Some materials will preferentially sputter neutral or positive particles which pick up electrons as they pass through the condensed cesium layer on the surface of the cathode, producing the negatively charged beam.