Split-Pole Spectrograph: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
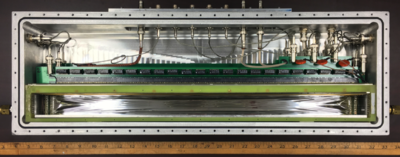
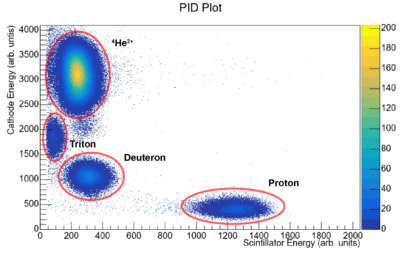
consists of an ion drift chamber with a set of delay lines to detect the position of a particle along the focal plane and a plastic scintillator to detect the energy of the incoming particle. Using the energy loss of the particle through the ion chamber with the energy deposited in the scintillator, particles of different charges and masses can be identified. | consists of an ion drift chamber with a set of delay lines to detect the position of a particle along the focal plane and a plastic scintillator to detect the energy of the incoming particle. Using the energy loss of the particle through the ion chamber with the energy deposited in the scintillator, particles of different charges and masses can be identified. | ||
The typical pressure of the drift chamber is 70 to 300 Torr of isobutane gas [HC(CH3)3]. The pressure controls the density of the gas and affects the bias voltage, it further affects the drift velocity. Here is a table of pressure and bias voltages. | The typical pressure of the drift chamber is 70 to 300 Torr of isobutane gas [HC(CH3)3]. The pressure controls the density of the gas and affects the bias voltage, it further affects the drift velocity. Here is a table of pressure and bias voltages (data taken from the Ph.D. thesis of Erin Good). | ||
{|class='wikitable' | {|class='wikitable' | ||
Revision as of 21:53, 27 May 2023
 Annotated picture of the SE-SPS, An plain picture is here : File:SPS Magnet.png |
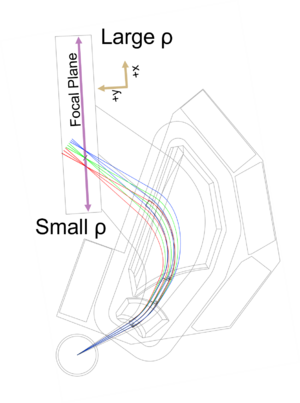 SE-SPS COSY simulation. An plain picture is here File:SPS Sketch With Cosy.png |
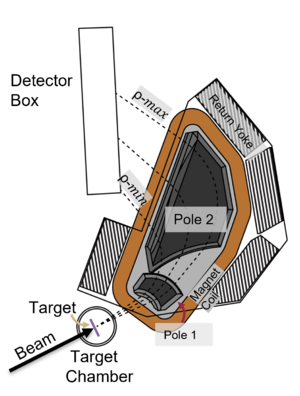
The Super Enge Split-Pole Spectrograph [1] [2] [3] was originally located at the Wright Nuclear Structure Laboratory (closed at 2013), at Yale University. It was moved to FSU in the fall of 2013. It consists of a reaction chamber, a split-pole magnetic spectrograph, a position-sensitive ionization drift chamber, and a plastic scintillator. It has an angular acceptance of 128 msr (vertical ±40 mrad, horizontal ±80 mrad). The maximum B-field is 1.63 T with a radius of curvature from 511 mm to 920 mm. The mean radius is 600 mm.
The Super Enge Split-Pole Spectrograph is an upgrade of the Yale Enge SPS. The major change is the redesign of the backward silicon detector array to the SABRE.
Magnet
The SPS contains 2 dipole magnets: pole-1 and pole-2. The magnet can be rotated from 0 to 55 degrees in the lab. The magnetic field has an upper limit of 1.63 T (or 16.3 kG).
Focal plane detector
The focal plane detector [4] [5] consists of an ion drift chamber with a set of delay lines to detect the position of a particle along the focal plane and a plastic scintillator to detect the energy of the incoming particle. Using the energy loss of the particle through the ion chamber with the energy deposited in the scintillator, particles of different charges and masses can be identified.
The typical pressure of the drift chamber is 70 to 300 Torr of isobutane gas [HC(CH3)3]. The pressure controls the density of the gas and affects the bias voltage, it further affects the drift velocity. Here is a table of pressure and bias voltages (data taken from the Ph.D. thesis of Erin Good).
| Gas pressure (Torr) | Anode bias (V) | Cathode bias (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 70 | +1050 to +1035 | -550 to -500 |
| 80 | +1150 | -550 |
| 100 | +1250 | -600 |
| 110 | +1200 to 1320 | -620 to -600 |
| 125 | +1425 | -650 |
| 130 | +1360 | -725 |
| 150 | +1500 | -700 |
There are two position-sensitive delay lines in the focal plane detector. By reconstructing the particle trajectory using the position information of both delay lines, the resolution can be enhanced by correcting for the kinematic shift of the reaction.
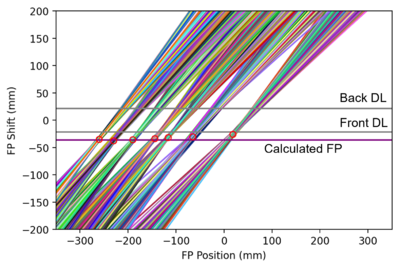
|
|
| Simulated rays near the focal plane. | An animation on the shift of the focal panel. An optimum is reached at FP = -42 mm. |
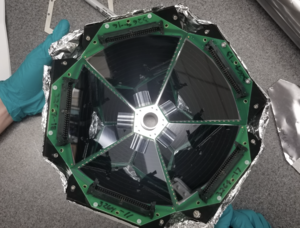
SABRE
The Silicon Array for Branching Ratio Experiments
SABRE is a silicon array designed around branching ratio experiments with the SPS. SABRE sits at backwards angles from the target, and covers roughly 30% of 4pi. SABRE has both thick and thin dead-layer detectors, with the thin dead-layer detectors capable of reaching ~200 keV thresholds for protons and deuterons.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168900221002837
SPS Experiment Guide
Media:SPS_Experiment_Guide.pdf
SPS Operating Procedures
I created this section as a place to store procedures for the chamber swaps, however, I expect there are other things we might want to document here. -p
Repositories
Contact
- Jeff Blackmon mailto:blackmon@lsu.edu
- Ingo
- who should be contacted?
References
- ↑ H.A. Enge, NIM 162, 161 (1979) https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(79)90711-0
- ↑ H. A. Enge, NIM 187, 1 (1981) https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(81)90465-1
- ↑ J. E. Spencer and H. A. Enge, NIM 49, 181 (1967) https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(67)90684-2
- ↑ C. Marshal et. al, IEEE Tran. Inst. and Meas. 68, 533 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2018.2847938
- ↑ R. G. Markham and R. G. H. Robertson, NIM 129, 131 (1975) https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(75)90122-6