Split-Pole Spectrograph: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
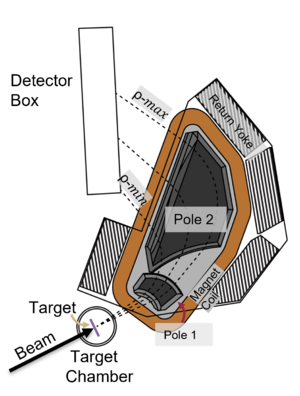
The Split-Pole Spectrograph consists of a reaction chamber, a split-pole magnetic spectrograph, ionization chamber, and a plastic | [[File:SPS Pictue Annotated.png|thumb|Annotated picture of the SE-SPS]] | ||
The Split-Pole Spectrograph consists of a reaction chamber, a split-pole magnetic spectrograph, an ionization chamber, and a plastic scintillator. | |||
The magnet can be rotated from 0 to 55 degrees in the lab. The magnetic field has an upper limit of 14.5 kG. | The magnet can be rotated from 0 to 55 degrees in the lab. The magnetic field has an upper limit of 14.5 kG. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 8: | ||
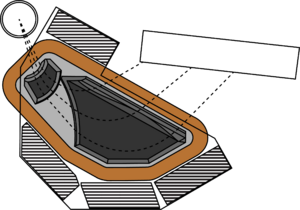
[[File:SPS Magnet.png|thumb|right|SE-SPS Magnet]] | [[File:SPS Magnet.png|thumb|right|SE-SPS Magnet]] | ||
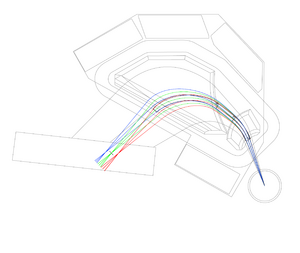
[[File:SPS Sketch With Cosy.png|thumb|SE-SPS COSY simularion]]. | [[File:SPS Sketch With Cosy.png|thumb|SE-SPS COSY simularion]]. | ||
== Focal plane detector == | == Focal plane detector == | ||
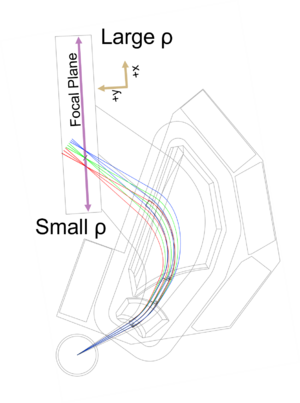
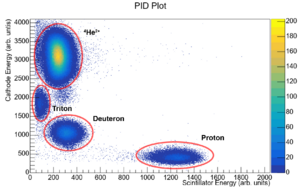
The focal plane detector consists of an ion chamber with a set of delay lines to detect the position of a particle along the focal plane and a plastic scintillator to detect the energy of the incoming particle. Using the energy loss of the particle through the ion chamber with the energy deposited in the scintillator, particles of different | The focal plane detector consists of an ion chamber with a set of delay lines to detect the position of a particle along the focal plane and a plastic scintillator to detect the energy of the incoming particle. Using the energy loss of the particle through the ion chamber with the energy deposited in the scintillator, particles of different charges and masses can be identified. | ||
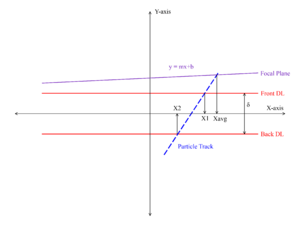
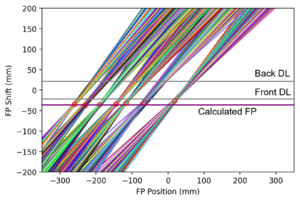
There are two position sensitive delay lines in the focal plane detector. By reconstructing the particle trajectory using the position information of both delay lines, the resolution can be enhanced by correcting for the kinematic shift of the reaction. | There are two position-sensitive delay lines in the focal plane detector. By reconstructing the particle trajectory using the position information of both delay lines, the resolution can be enhanced by correcting for the kinematic shift of the reaction. | ||
[[File:SPS Picture ray.png|thumb]] | [[File:SPS Picture ray.png|thumb]] | ||
Revision as of 17:55, 27 May 2023
The Split-Pole Spectrograph consists of a reaction chamber, a split-pole magnetic spectrograph, an ionization chamber, and a plastic scintillator.
The magnet can be rotated from 0 to 55 degrees in the lab. The magnetic field has an upper limit of 14.5 kG.
Magnet
.
Focal plane detector
The focal plane detector consists of an ion chamber with a set of delay lines to detect the position of a particle along the focal plane and a plastic scintillator to detect the energy of the incoming particle. Using the energy loss of the particle through the ion chamber with the energy deposited in the scintillator, particles of different charges and masses can be identified.
There are two position-sensitive delay lines in the focal plane detector. By reconstructing the particle trajectory using the position information of both delay lines, the resolution can be enhanced by correcting for the kinematic shift of the reaction.
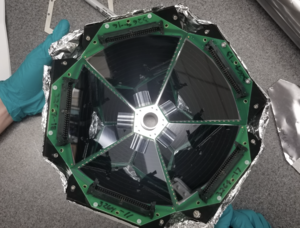
SABRE
The Silicon Array for Branching Ratio Experiments
SABRE is a silicon array designed around branching ratio experiments with the SPS. SABRE sits at backwards angles from the target, and covers roughly 30% of 4pi. SABRE has both thick and thin dead-layer detectors, with the thin dead-layer detectors capable of reaching ~200 keV thresholds for protons and deuterons.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168900221002837
SPS Experiment Guide
Media:SPS_Experiment_Guide.pdf
SPS Operating Procedures
I created this section as a place to store procedures for the chamber swaps, however, I expect there are other things we might want to document here. -p
Repositories
Contact
- Jeff Blackmon mailto:blackmon@lsu.edu
- Ingo
- who should be contacted?